ARCA kindly thanks archaeologist and academic translator Folkert Tiarks of Toptransarchaeo for his assistance in translating this blog report from English into German for ARCA's German-speaking readership.
Am 29. November 2016 wurde ARCA durch Christos Tsirogiannis darüber informiert dass er vier antike, potentiell illegale Objekte identifiziert habe, die
am 14. Dezember 2016 bei Gorny & Mosch in München versteigert werden sollen. Jedes dieser vier Objekte lässt sich auf Fotos aus den beschlagnahmten Archiven von Gianfranco Becchina und Robin Symes nachweisen.
Los 19 Etruskische Bronzestatue eines Jünglings, Mitte 5. Jahrhundert vor Christus
 |
| Abbildung 1 - Gorny & Mosch 14. Dezember 2016 Auktions-Los 19 |
Die Sammlungsgeschichte wird wie folgt angegeben:
"Ex Sammlung R.G., Deutschland. Bei Royal Athena Galleries, New York, Catalogue XXI, 2010, 43. Ex Sotheby´s Catalogue of Antiquities 13. Juli 1981, 341."
Jerome Eisenberg, Herausgeber der Zeitschrift Minerva und Eigentümer der Royal Athena Galleries in New York City, ist ein Name, der in der Vergangenheit als Käufer oder Verkäufer von Antiken umstrittener Herkunft zur Sprache gekommen ist. Für weitere Informationen zu einigen der in letzter Zeit von der Gallery erworbenen Objekte klicken sie bitte
hier, hier, hier und
hier.
 |
| Abbildung 2 - Symes Archiv Foto |
Kürzlich erkannte Tsirogiannis Los 19 (Bild 1) im Symes Archiv (Bild 2), während dieses Loss noch im Oktober 2010, zusammen mit einigen anderen Antiken, deren Bilder in den Archiven von Medici und Becchina auftauchten von der Royal Athena Galleries angeboten wurde. Im Januar 2011 wurden diese Identifizierungen von Professor David Gill in seinem Blog
"Looting Matters" vorgestellt und in der italienischen Presse durch den auf Kunst und Korruption spezialisierten Journalisten Fabio Isman im
"Giornalle dell’arte" publik gemacht. Zusammen mit jeder dieser Bekanntmachungen wurde ein aus dem Symes Archiv stammendes Foto der etruskischen Bronzefigur veröffentlicht.
Die Tatsache, dass dieses Objekt jetzt, fünf Jahre nach der ersten Identifizierung, wieder zum Verkauf angeboten wird, bedeutet entweder dass die italienischen Behörden bei diesem einzelnen Objekt nicht tätig wurden oder dass der damalige Besitzer der Antike ausreichende Beweise vorlegen konnte die eine Einstufung als illegal gehandelte Antike verhinderten. Diese Information (sofern es sie gibt) wurde durch das Auktionshaus nicht in die Sammlungs-geschichte aufgenommen.
Los 87 Eine apulische rotfigurige Situla des Lykurgos-Malers. 360-350 v. Chr.
 |
| Abbildung 3 - Gorny & Mosch 14. Dezember 2016 Auktions-Los 87 |
Die Sammlungsgeschichte wird wie folgt angegeben:
"Aus der James Stirt Collection, Vevey in der Schweiz, erworben 1997 bei Heidi Vollmöller, Zürich."
 |
Abbildung 4 Gegenteil von Los 87 (links)
Becchina Archivfoto einer Situla (rechts) |
Das von Tsirogiannis zur Verfügung gestellte Foto aus dem Archiv Symes zeigt die Vase mit schweren Ablagerungen von Erde und Salz. Aus einer dem Archivfoto beigefügten hand-schriftlichen Notiz geht hervor, dass die Bilder am 18. März 1988 von Raffaele Montichelli an Gianfranco Becchina geschickt wurden.
Montichelli ist ein verurteilter Antikenhändler aus Tarent der über viele Jahre eine Partnerschaft mit Gianfranco Becchina unterhielt. Als Montichellis seriöser Beruf wird Grundschullehrer im Ruhestand erwähnt, dennoch scheint er aus den unrechtmäßigen Einnahmen mit illegal gehandelter Kunst genug l Geld verdient zu haben,
dass er in einigen von Italiens exklusiveren Gegenden von Florenz und Rom lukrative Immobilien kaufen konnte. Diese wurden später durch die italienischen Behörden beschlagnahmt.
Es ist bemerkenswert, dass in der Sammlungsgeschichte dieses Lots der Abschnitt über Becchina vor der im Verkaufskatalog von Gorny & Mosch erwähnten Herkunft aus einem Auktionshaus datiert. Hat Vollmöller, als sie das Objekt in Kommission nahm, die Kaufgeschichte, von wem die Situla erworben wurde, weggelassen oder haben Gorny & Mosch sie absichtlich ausgelassen?
Lot 88 An Apulian red-figure bell-krater of the Dechter Painter. 350 - 340 B.C.E.
 |
| Abbildung 4 - Gorny & Mosch 14. Dezember 2016 Auktions-Los 88 |
Die Sammlungsgeschichte wird wie folgt angegeben:
Ex Galerie Palladion, Basel; ex Privatsammlung von Frau Borowzova, Binnigen in der Schweiz, erworben 1976 von Elie Borowski, Basel.
 |
Abbildung 6 - Becchina Archiv foto
dieses Kraters |
Palladion Antike Kunst (man beachte den leicht korrigierten Namen der Galerie)
wurde von Gianfranco Becchina aus Basel, Schweiz, geleitet obwohl als offizielle Besitzerin der Schweizer Galerie
Ursula “Rosie“ Juraschek, Becchinas Ehefrau geführt wurde.
Tsirogiannis stellte ein aus dem Becchina Archiv stammendes, auf den 4. April 1989 datiertes Foto dieses Kraters (Abb.6 ) zur Verfügung. Wieder sehen wir ein mit Erd-und Salzablagerungen bedecktes Objekt mit einigen Fehlstellen. Man beachte dass die Datierung des unrestaurierten Objektes in das Jahr 1989 nicht mit dem Datum übereinstimmt, an dem das Objekt in die Sammlung Elie Borowski aufgenommen wurde.
Elie Borowski, dessen umfangreiche Sammlung von Gegenstanden aus dem Mittleren Osten später den Großteil des Bible Land Museums bildete, starb im Jahr 2003. Vertraut mit den Schattenseiten des Antikenhandels, teilte die ehemalige Kurator der Antiken-Abteilung des Getty Museums, Marion True, den italienischen Behörden mit, dass auch Borowski, ein in Basel/Schweiz, ansässiger Antiken-händler, ein Kunde Gianfranco Becchinas sei.
Interessanterweise unternahm Borowski eine diskrete Reise nach Gubbio um sich dort die erst kurz zuvor aus dem Meer geborgene Bronze anzusehen, bevor diese ihren endgültigen Weg nach Malibu antrat. Aber Borowskis Eintauchen in eine mögliche Betrügerei war hier noch nicht zu Ende. Sein Name erscheint in einem inzwischen zu Berühmtheit gelangtem Organigramm von Händlern, einem handgeschriebenen Schaubild des illegalen Handels, das von den italienischen Behörden im wohnung von Danilo Zicchi beschlagnahmt wurde. Sein Name
wurde auch in Verbindung gebracht mit Raubantiken aus der Türkei.
Los 127 Gedrungenes Alabastron der Gnathia-Ware mit dem Bildnis einer geflügelten Frau mit Sakkos. Dem Maler der weißen Hauben zugeschrieben. Apulien, 320-310 v. Chr.
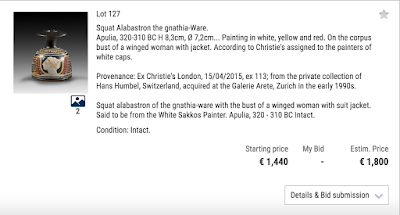 |
| Abbildung 7 - Gorny & Mosch 14. Dezember 2016 Auktions-Los 127 |
Die Sammlungsgeschichte wird wie folgt angegeben:
Ex Christie´s London, 15.04.2015, ex 113; aus der Privatsammlung von Hans Humbel, Schweiz, erworben bei der Galerie Arete, Zürich in den frühen 1990er Jahren.
 |
Abbildung 8 - Becchina Archiv foto
dieses alabastron |
Zusammen mit anderen im Hintergrund sichtbaren Antiken, ist dieses Objekt auch auf einem von Tsirogiannis zur Verfügung gestellten Foto aus dem Becchina Archiv zu sehen. Das Foto datiert vom 24. September 1988 und wurde ebenfalls vom verurteilten Händler Raffaele Montichelli an Gianfranco Becchina geschickt.
Wie bei den vorausgegangenen Losen, datiert das Datum auf dem Foto vor die von Gorny & Mosch angegebene Sammlungsgeschichte. Dies lässt mich vermuten, dass die Sammlungsgeschichten aller vier Objekte in Details nur sehr spärlich angegeben wurden.
Wie Los 19 dieser Identifizierung, ist dieses das zweite Mal, dass dieses bestimmte Objekt vor einer bevorstehenden Auktion identifiziert wurde.
Aber die Spur wird noch interessanter.
Am 11. April 2015 veröffentlichte ARCA Tsirogiannis originale Identifizierung des Alabastrons mit folgender, von Christies zur Verfügung gestellter Provenien-zangabe.
"Durch den gegenwärtigen Eigentümer im Jahr 1998 vom Petit Musee, Montreal, erworben".
Das Objekt war ein Teil des aus zwei Vasen bestehenden Loses 113, das am 15. April 2016 in der Antiken-Auktion von Christie’s in London versteigert wurde. Ein von ARCA aufgenommener screenshot (Bild 9) der bei der urprünglichen Identifizierung vom April 2015 verwendet wurde, wird unten nochmals abgebildet.
 |
| Abbildung 9 - Screenshot der Website von Christie 11. April 2015 |
Am 15. April 2015 wurde das Alabastron mit folgender Bekanntmachung im Auktionssaal von der Auktion zurückgezogen: "Das Los wurde zurückgezogen".
Wenn man heute Christie‘ s URL anklickt, die immer noch mit der letztjährigen Auktion verlinkt, sieht man, dass das Foto gelöscht und durch ein anderes (Bild 10) ersetzt wurde, das nur die birnenförmige Flasche aus Los 113 zeigt.
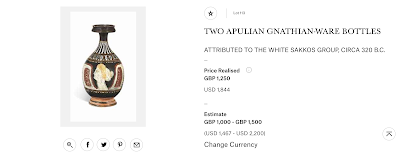 |
Abbildung 10 - Screenshot der Website von Christie 30. November 2016
|
Darüber hinaus wurde die Bekanntmachung der Rücknahme durch diese ersetzt (Abb. 11).
 |
| Abbildung 11 - Screenshot der Website von Christie 30. November 2016 |
Seltsamerweise führen Gorny & Mosch als Provenienz "Ex Christie’s London, 15.April 2015".
Hat Christie’s den Verkauf im April 2015 durchgesetzt anstatt ihn zurückzunehmen? Oderhaben Gorny & Mosch die unbeendete Auktion aufgeführt um ihrer eigenen Auflistung mehr Glaubwürdigkeit zu verleihen, jetzt, da sich der Besitzer des Stückes sich entschlossen hat, das Stück in Deutschland zu…Wer hat aus welchem Grund das Bild des Alabastrons gegen das der birnenförmigen Flasche ausgetauscht?
Und was ist mit Christie’s früherer Provenienzangabe, die das „Petit Musee, Motreal“ nannte, von dem der jetzige Besitzer das Stück im Jahr 1988 erwarb? War diese Sammlungsgeschichte eine Fiktion, die später unbequem für den Besitzer und das aktuelle Auktionshaus wurde?
ARCA hofft, dass durch die kontinuierliche Bekanntgabe der Häufigkeit mit der illegale Antiken die Unregelmäßigkeiten in ihrer Provenienz aufweisen wie dies bei diesen Identifizierungen der Fall ist, auf den legalen Kunstmarkt gelangen, Auktionshäuser und Sammler gezwungen werden ,die genauen und strengen Anforderungen bei der Angabe der Sammlungsgeschichte ihrer Objekt einzuhalten, so dass neue Käufer nicht weiter Objekte waschen, um den Handel mit illegalen Antiken zu unterstützen.
Abschließend sei gesagt, dass sich Tsirogiannis, ein in Cambridge ansässiger forensischer Archäologe und Dozent beim
Aufbaustudiengang der ARCA "Kriminalität gegen die Kunst und Kulturgüter-schutz", seit 2007 darum bemüht, Antiken illegaler Herkunft zu identifizieren, die sich in denjenigen Museen, Sammlungen, Galerien und Auktionshäusern befinden, die durch die beschlagnahmten Archive von Giacomo Medici, Robin Symes, Christos Michaelides und Gianfranco Becchina zurückverfolgt werden können.
Tsirogiannis hat Interpol über seine Identifizierungen informiert verbunden mit der Bitte, sowohl die italienschen als auch die deutschen Behörden ebenfalls formell darüber zu informieren. Hoffen wir, dass Gorny & Mosch das Objekt zurückziehen und künftig ihrer Sorgfaltspflicht bei der Prüfung der Einlieferer von Objekten besser nachkommen.
Von Lynda Albertson
 Becchina,Becchina archive,George Ortiz,illicit trade in antiquities,illicit trafficking,restitution,Sotheby's
Becchina,Becchina archive,George Ortiz,illicit trade in antiquities,illicit trafficking,restitution,Sotheby's
 No comments
No comments











































