Tuesday, November 08, 2016 -  Auction Alert,Becchina archive,Bonhams,Christo Michaelides,Christos Tsirogiannis,James Chesterman,London,Medici Dossier,Robin Symes
Auction Alert,Becchina archive,Bonhams,Christo Michaelides,Christos Tsirogiannis,James Chesterman,London,Medici Dossier,Robin Symes
 No comments
No comments
 Auction Alert,Becchina archive,Bonhams,Christo Michaelides,Christos Tsirogiannis,James Chesterman,London,Medici Dossier,Robin Symes
Auction Alert,Becchina archive,Bonhams,Christo Michaelides,Christos Tsirogiannis,James Chesterman,London,Medici Dossier,Robin Symes
 No comments
No comments
Auction Alert - Bonhams Auction House - An il(licit) Etruscan Terracotta Antefix
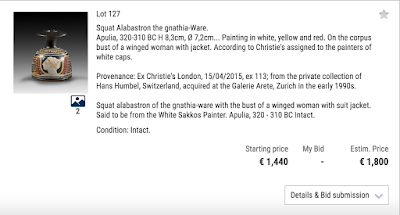
On November 7, 2016 ARCA was informed by Christos Tsirogiannis that he had identified a new potentially tainted antiquity scheduled to be auctioned by Bonhams auction house in London on November 30, 2016 traceable to the confiscated Giacomo Medici archive.
That item is Lot 14, An Etruscan Terracotta Antefix
A screenshot of the provenance/collection history details are added here:
Etruscan buildings were often decorated with polychrome terracotta elements. Antefixes, such as this one on auction, were placed at the end of the rows of roofing tiles located along the eaves of the roof. Usually made in molds, many took the form of male or female mythological characters.
Since 2007 Tsirogiannis, a UK-based Greek forensic archaeologist and summer lecturer with ARCA's Postgraduate Program in Art Crime and Cultural Heritage Protection, has sought to identify antiquities of illicit origin in museums, collections, galleries and auction houses that can be traced to the confiscated Giacomo Medici archives and the related Robin Symes-Christos Michaelides and Gianfranco Becchina archives.
Each of these dealer's archives provide insight inside a network of illicit trade in antiquities and, when combined, include thousands of ancient objects from all over the world which have passed through the hands of smugglers, middlemen, and antiquities dealers who "laundered” illicit objects through the licit market.
 |
| Two images from image from the confiscated Medici archive alongside the Bonham Auction Object Lot. |

An expert on terracotta figurines, James Chesterman collected avidly and was the author of Classical Terracotta Figures published by Littlehampton Book Services Ltd, 1974. In 1984 the Fitzwilliam Museum purchased more than 100 Greek and Roman terracotta figurines from Chesterman's collection, in what is likely to be, in the museum's own words, the last major private collection to enter the Museum.
Who were some of James Chesterman's sources for antiquities?
Conducting a quick search (meaning far from comprehensive) of objects from the Chesterman's collection that have come up on auction tells us a little about some of his sources.
We know this collector was buying from Jean Mikas, Paris; thence by descent to his nephew, George Krimitsas, Paris in 1982
 |
| Medici Archive image provided by Dr. Christos Tsirogiannis |
After the closing of his Rome Gallery, Giacomo Medici entered into partnership with Geneva resident Christian Boursaud and opened Hydra Gallery in Geneva in 1983 (Silver 2009: 139).
This Swiss gallery then began consigning material supplied by Medici for sale on the London market, predominantly through Sotheby's. (Silver 2009: 121-2, 139; Watson and Todeschini 2007: 27). Watson and Todeschini estimated that during the period of the 1980's Medici was the source of more consignments to Sotheby’s London than any other vendor (Watson and Todeschini 2007: 27).
If the collection history on the Bonhams Lot is accurate, then Medici's pieces were also appearing on the Paris antiquities market during that same period. If it isn't, then this object is missing a passage from its London history.
Dr. David Gill also has analyzed this new sighting, adding his own research in this Looting Matters blog post.
Dr. David Gill also has analyzed this new sighting, adding his own research in this Looting Matters blog post.
Christos Tsirogiannis also matched a Greek bust of Hermes on offer at Bonhams found in the Gianfranco Becchina archive in October 2014.
Many have argued that Dr. Tsirogiannis tactics of naming potentially looted objects from the archives via ARCA's blog, David Gill's Looting Matters and on occasion Neil Brodie's Market of Mass Destruction, places auction houses at a disadvantage and should be construed as unfair given the market does not have direct access to the photos in these archives. A valid point, but given the frequency illicit antiquities continue to penetrate the legitimate art market, we hope this will lead auction houses to consider more stringent reporting requirements of their consignors to insure that they do not inadvertently support the illicit antiquities trade.
In closing, given the proven lucrative nature of unprovenanced antiquities on the open market, Tsirogiannis has notified Interpol who in turn will notify the Italian authorities of his new identifications. Here's hoping that his continued spotlight, however awkward it is for everyone, will serve as a recurring reminder that we still have a long way to go before the licit art market is cleaned up.
By: Lynda Albertson
----------------------
Bibliography:
Lindros Wohl Birgitta, Three female Head antefixes from Etruria,
in The Getty Museum Journal, 12, 1984, pp. 114-116.
Pallottino Massimo, Giuseppe Foti, Antonio Frova, Franco Panvini Rosati (sous la dir. de) Art et civilisation des Étrusques, octobre-décembre 1955, cat. adapté et traduit par Jean Charbonneaux et Marie-Françoise Briguet, Paris
Silver Vernon The lost chalice: the real-life chase for one of the world's rarest masterpieces: a priceless 2,500-year-old artifact depicting the fall of Troy
Harper - 2010
Watson Peter and Todeschini Cecilia The Medici conspiracy: the illicit journey of looted antiquities from Italy's tomb raiders to the world's greatest museums
PublicAffairs - 2007